Interesting Facts About Earths Troposphere
Earth’s troposphere is one of the most interesting and dynamic parts of our planet. It’s the lowest part of the atmosphere, and it’s where most of the weather we experience on a day-to-day basis takes place. It’s also the layer of the atmosphere that contains most of the water vapor and dust particles that can create beautiful sunsets and rainbows. In this article, we’ll explore some of the most fascinating facts about Earth’s troposphere. From the role it plays in weather formation to the incredible phenomena that can occur within it, you’ll be amazed by the diversity of the troposphere. Make sure to visit our interesting facts about Earths Stratosphere blog post.
Uncovering the Secrets of Earth’s Troposphere
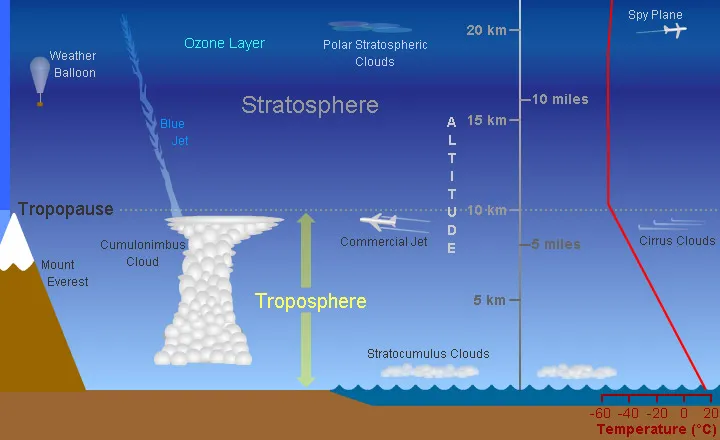
The troposphere is the layer of Earth’s atmosphere closest to the surface. It plays a vital role in maintaining the global climate and is host to a variety of weather systems. In order to understand how these systems interact and affect the planet, it is important to uncover the secrets of the troposphere.
First, it is important to understand the structure and composition of the troposphere. It is composed of nitrogen, oxygen, and water vapor, and is bounded by the tropopause, which is the boundary between the troposphere and the stratosphere. The troposphere varies in thickness, ranging from around 8-17 kilometers, but is generally thicker near the equator and thinner near the poles. It is also home to clouds, aerosols, and other particulates.
The temperature of the troposphere decreases with altitude, a phenomenon known as the “lapse rate.” This is due to the fact that air pressure decreases with altitude, and as a result, air expands and cools as it rises. The average lapse rate is 6.5°C per kilometer, but it can vary depending on the season and latitude.
The troposphere is also home to a variety of weather systems, such as fronts, storms, and thunderstorms. These weather systems are driven by the global circulation of the atmosphere, which is driven by the unequal heating of the Earth’s surface. The circulation of the atmosphere creates areas of high and low pressure, which can cause winds and other weather phenomena.
Finally, the troposphere is home to a variety of greenhouse gases, including carbon dioxide, methane, and water vapor. These gases absorb and retain heat, which helps to regulate the global climate. Without these gases, the Earth’s temperature would be much colder than it currently is.
The troposphere is an incredibly complex layer of the atmosphere, and understanding its secrets is essential to understanding the global climate. By studying the structure, composition, and weather systems of the troposphere, we are better able to understand how our planet works and how we can protect it.
Fascinating Facts About Our Planet’s Atmospheric Layer
and objective
The atmosphere is a critical component of the Earth’s environment, providing the air we breathe and playing a key role in regulating the Earth’s climate. Here are some fascinating facts about our planet’s atmospheric layer:
- The atmospheric layer is composed of 78% nitrogen and 21% oxygen with trace amounts of other gases such as carbon dioxide and argon.
- The atmosphere is divided into four layers: troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, and thermosphere. The troposphere is the lowest layer and contains the majority of the Earth’s weather and clouds.
- The atmosphere also contains water vapor, which helps to regulate the global climate by initiating a water cycle that transfers heat energy between the atmosphere and the surface of the Earth.
- The atmospheric layer plays a key role in moderating the temperature on Earth. In the absence of this layer, the Earth’s average temperature would be -18°C instead of the current 15°C average.
- The atmospheric layer also serves to protect the Earth from incoming radiation from the sun. This layer absorbs and reflects radiation from both the sun and space, preventing damage to the Earth’s surface.
- The atmosphere is constantly in motion due to air pressure and temperature differences, creating winds that move around the globe. These winds help to spread heat energy from the equator to the poles.
- The atmosphere is composed of multiple layers of gases, some of which contain ozone. Ozone helps to protect the Earth from harmful ultraviolet radiation from the sun.
- The atmosphere also plays a role in helping to regulate the Earth’s climate by trapping heat near the surface of the Earth, creating a phenomenon known as the “greenhouse effect”.
These facts illustrate the vital role the atmosphere plays in sustaining life on Earth. Without this layer, the Earth would be too cold for human life and the environment would be unable to sustain complex ecosystems.
Exploring the Mysteries of the Earth’s Lowermost Layer
The Earth’s lowermost layer, the mantle, is an enigma shrouded in mystery. It has been the source of much scientific speculation and debate over the years, and continues to challenge our understanding of our planet’s inner workings.
The mantle is located between the Earth’s inner core and outer crust. It is about 2,900 kilometers thick and is composed mostly of silicate rocks, such as olivine and pyroxene. Despite its immense size, the mantle is largely unseen. It is too deep for us to observe directly, and we must rely on indirect methods to study it.
One way scientists have been able to learn more about the mantle is by studying seismic waves. Seismic waves are generated by earthquakes and other events, and they travel through the Earth’s interior, revealing information about the structure and composition of the mantle. By analyzing the data from these seismic waves, scientists have been able to map out the internal structure of the mantle, as well as the speed with which different materials move through it.
Seismic waves have also revealed evidence of convection currents in the mantle. Convection currents occur when hot material rises and cool material sinks. In the mantle, these currents are thought to be responsible for the gradual movement of tectonic plates and the formation of new mountains and volcanoes.
The mantle also plays an important role in the Earth’s climate. It contains vast amounts of carbon stored in the form of carbon dioxide, methane, and other compounds. When these compounds are released into the atmosphere, they trap heat and contribute to global warming.
Despite these advances in our understanding, the mantle still holds many secrets. Much of its interior remains a mystery, and further research is needed to fully unlock its secrets.